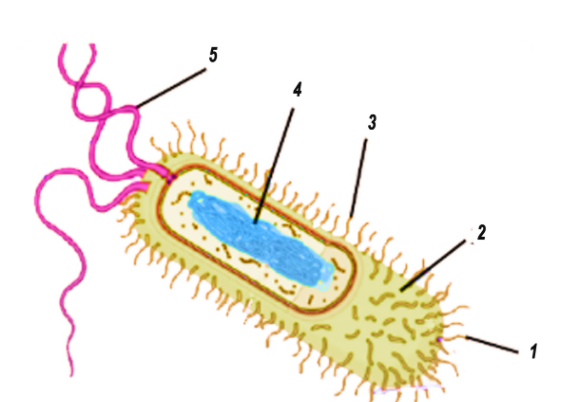
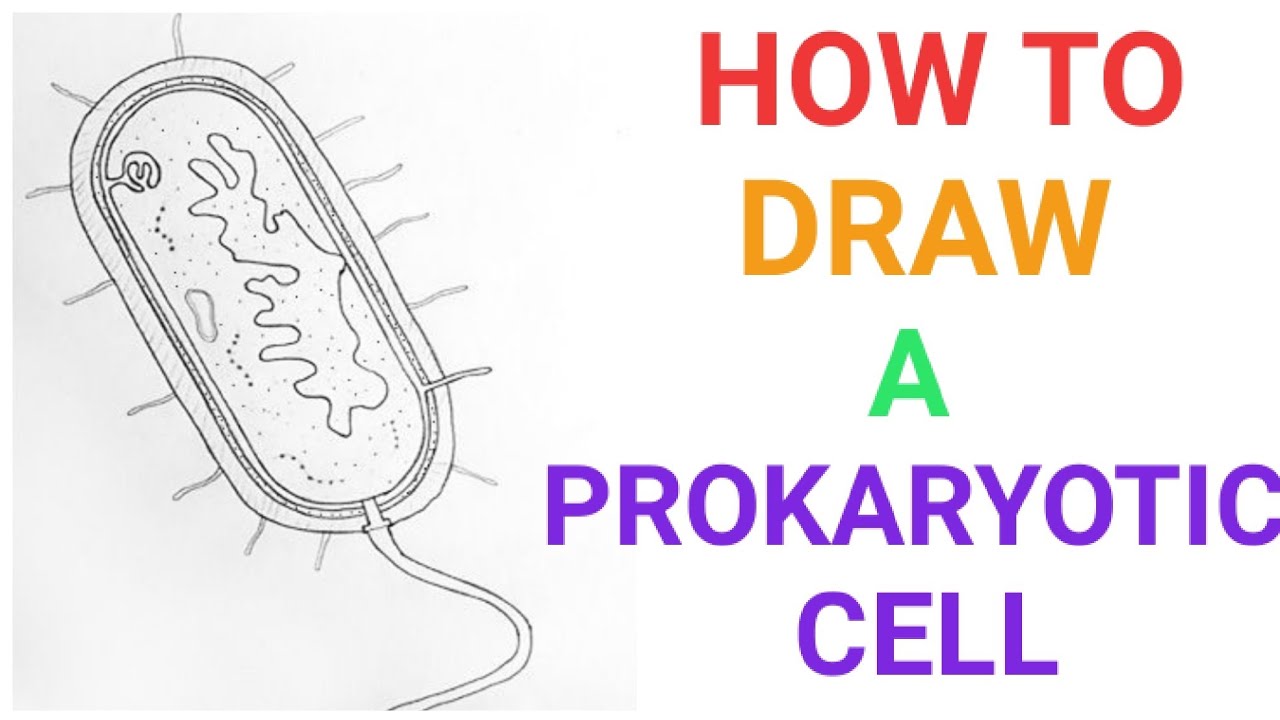
40 prokaryotic cells label
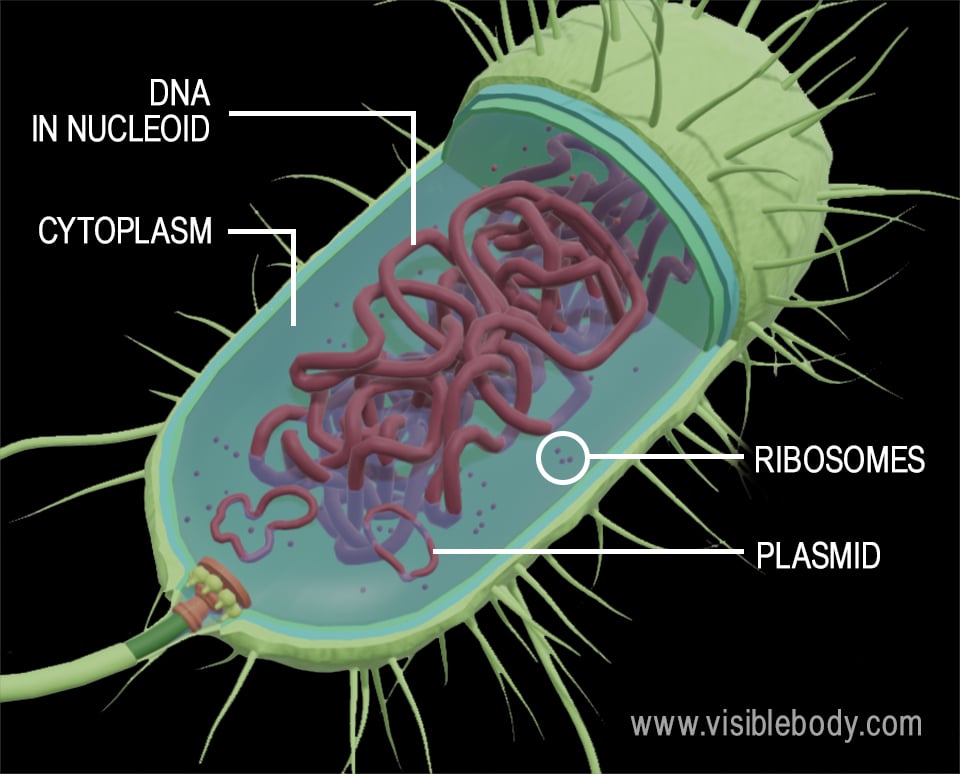
Cytoplasm: structure and function | Kenhub Cells of animals, plants and fungi are known as eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes contain a well defined nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane. Prokaryotic cells are found in bacteria. Instead of a well-defined nucleus, the prokaryotic cells contain a nucleoid, which is a single loop of DNA that lies free within the cytoplasm of the cell. The difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? - Live Science What are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? All living things can be divided into three basic domains: Bacteria, Archaea and Eukarya. The primarily single-celled organisms found in the Bacteria and...
Plasmid - Genome.gov Definition. 00:00. …. A plasmid is a small circular DNA molecule found in bacteria and some other microscopic organisms. Plasmids are physically separate from chromosomal DNA and replicate independently. They typically have a small number of genes — notably, some associated with antibiotic resistance — and can be passed from one cell to ...

Prokaryotic cells label
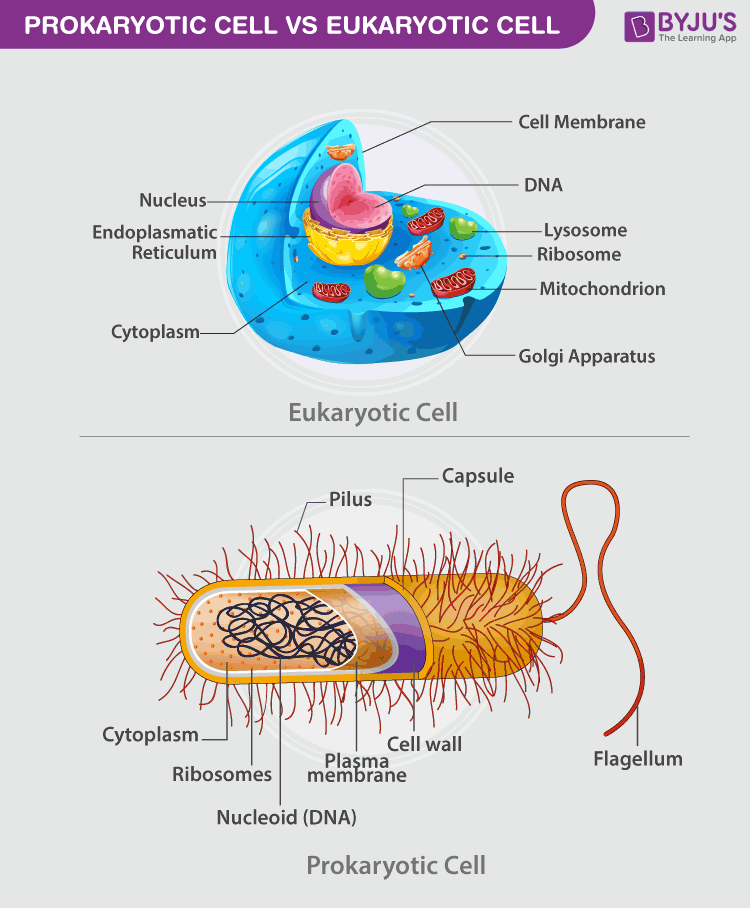
Eukaryotic Cells: Definition, Diagram, and Examples - Research Tweet Microorganism are divided into Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes. Organism that do not possess nucleus and lack organelles are called prokaryotes. Eukaryotic cells are those who contains nucleus as well as the organelles. Example of prokaryotes are Archaea and Eubacteria. Eukaryotic organism examples are Algae, Fungi, Plants, Protists and Animals. Eukaryotic Cells MCQ Quiz! - ProProfs Quiz Centrioles. 8. Prokaryotes are different from eukaryotic cells because they do not have membrane-bound nuclei. A. True. B. False. 9. Eukaryotic cells cannot produce energy. Plant Cell- Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram Eukaryotic cell sediment in the 90s while prokaryotic cell sediment in the 70s. Ribosomes found in the mitochondria and chloroplasts are as small as the prokaryotic ribosomes. Naturally, ribosomes are made up of two subunits i. e small and large subunits, both classified according to their sedimentation rates by the S unit.
Prokaryotic cells label. Prokaryotic Cells Quiz - ProProfs Quiz Welcome to this unique "Prokaryotic Cells Quiz" that is going to test your knowledge about prokaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are unicellular organisms that lack a membrane-bound nucleus, mitochondria, or any other membrane-bound organelle. They are divided into two domains; Archaea and Bacteria. What do you know about this particular organism? Plant Cell Parts Labeled - b442louispowell.blogspot.com Plant Cell Parts Labeled Plant cells are very rigid because of their cell wall a component that does not exist within animal cellsThe plant cell wall was inherited from our prokaryotic ancestor and became a highly specialized part of the cell. Parenchyma collenchyma and sclerenchyma. Eukaryotic Cell: Definition, structure and organelles | Kenhub There are two general classes of cells that exist: the self-sustaining simple cells known as prokaryotic (bacteria and archaea) and the more complex dependent cells known as eukaryotic. The eukaryotic cells types are generally found in animals, plants, algae, and fungi. Difference Between Prokaryotic Cell and Eukaryotic Cell Size. A prokaryotic cell is a small-sized cell of 1-10um. A eukaryotic cell is comparatively large in size, i.e., about10-100um. Endoplasmic Reticulum. The endoplasmic reticulum is absent in prokaryotes. Eukaryotes have the endoplasmic reticulum. Mitochondria. Mitochondria is absent in them. Mitochondria is present in eukaryotes.
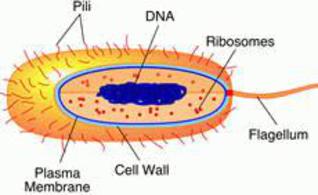
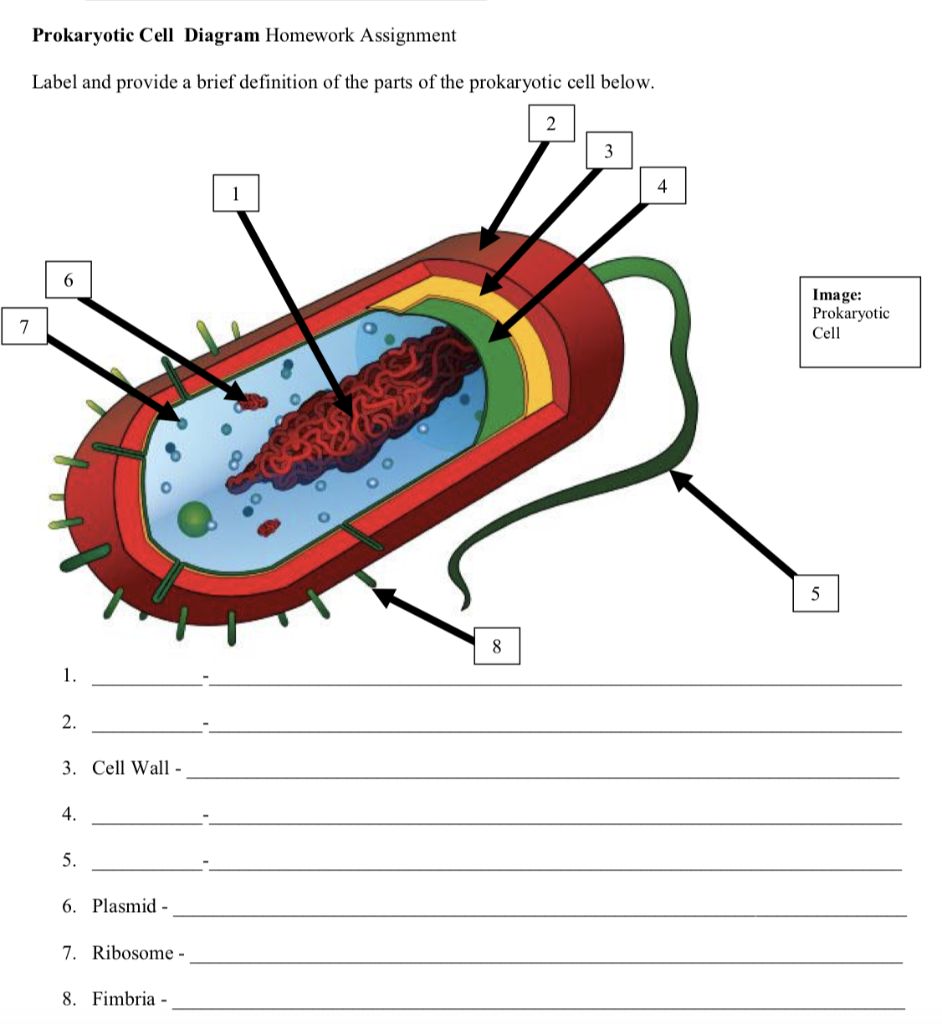
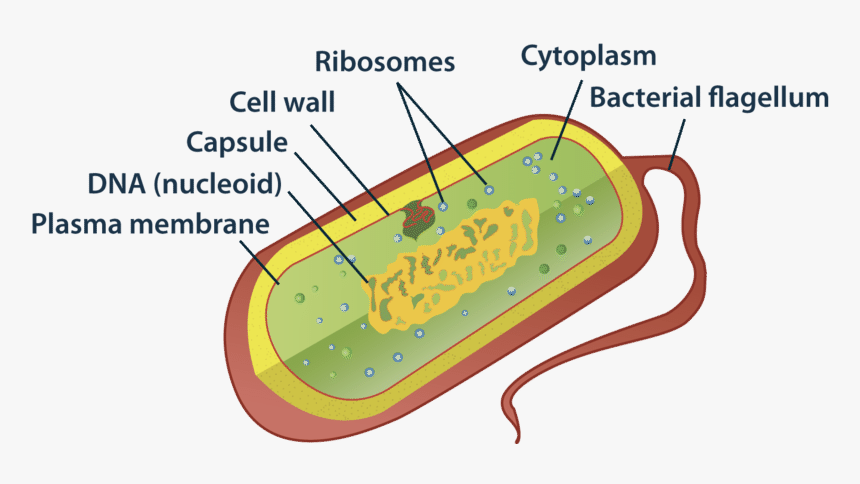
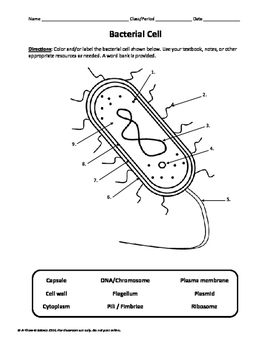
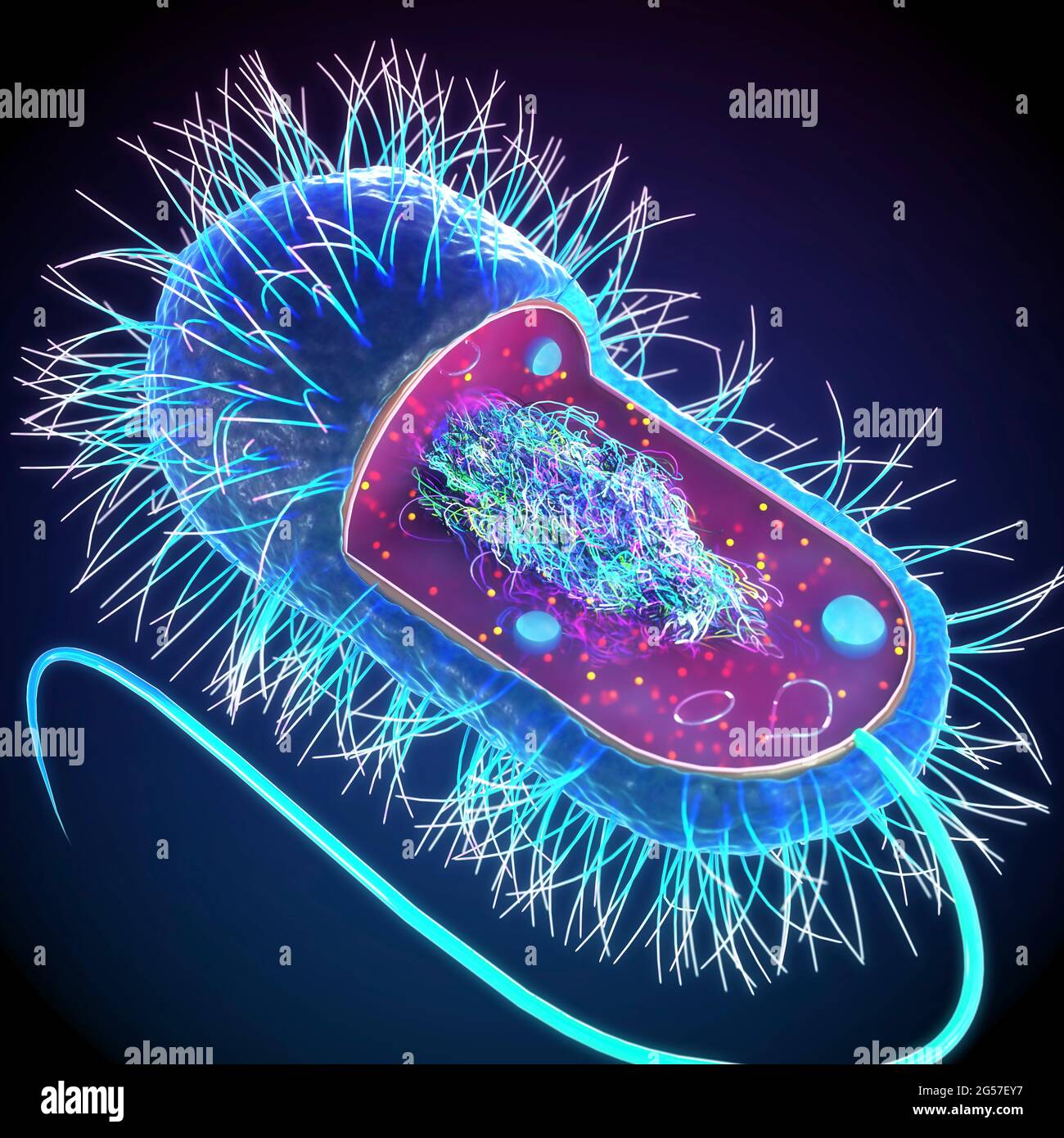
Label Worksheet Cell Prokaryotic Magnifies cells that are too small to see with the naked eye Based on the above word definitions, label the cells in Model 1 and Model 2 as prokaryotic or eukaryotic Labeling the Prokaryotic Cell . Cell Organelles- Definition, Structure, Functions, Diagram Animal Cell- Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram; Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes- Definition, 47 Differences, Structure, Examples; Amazing 27 Things Under The Microscope With Diagrams; Bacteria- Definition, Structure, Shapes, Sizes, Classification; ... In the case of prokaryotic cells, the ribosomes are of the 70S with the ... Prokaryotic Cell: Definition, Examples, and Structure - Research Tweet Prokaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells lack organelles and organelles such as mitochondria, chloroplast and nucleus, they are said to be unicellular. The DNA encapsulated in the nucleoid region of the cytoplasm is single stranded circular DNA, where the mode of reproduction is asexually through budding and binary fission. Bacterial Cell Label - label the bacterial cell key beautiful solved ... Bacterial Cell Label - 16 images - unlabeled bacteria cell diagram data diagram medis, do prokaryotic cells have a nucleus anatomy and physiology class, glycopedia, 33 label a bacterial cell labels for you,
Prokaryotic Cell Without Labels - 18 images - cell organelles cells the ... [Prokaryotic Cell Without Labels] - 18 images - pin on cells, bacteria diagram labeled clipart best, difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells biology exams 4 u, difference between plant and animal cells cells as the basic units of, Bacterial Cell Label - unlabeled bacteria cell diagram data diagram ... Bacterial Cell Label - 16 images - prokaryotic bacteria cell 1, multiple choice diagram quiz on bacterial cell biology multiple, bacteria, label the bacterium cell, Identify and label the key features/organelles of cells from plants ... A cell that lacks a membrane-bound nucleus is a prokaryotic cell. The word prokaryote is a combination of the Greek words pro, which means "before," and karyon, which means "nut or kernel." Organisms that contain prokaryotic cells are referred to as prokaryotes. Most prokaryotes are single-celled, although some are multicellular. Prokaryotic Cell Label Worksheet Search: Label Prokaryotic Cell Worksheet. To Do List: (Prokaryotes) Plate Cultures: Seal with parafilm Read the passage below Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles; prokaryotic cells do not Jack0m/Getty Images The two groups of prokaryotic organisms are so different from each other that they are grouped into different domains The two groups of prokaryotic organisms are ...
Eukaryotic Cell: Structure, Characteristics & Diagram - Embibe Plants, fungi and protozoa are some of the examples that have eukaryotic cells. Cells are generally classified into two types which are eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells are considered to be more advanced cells and are found in higher organisms. Eukaryotic cell is a chapter that is taught in CBSE class 11 Biology.
Prokaryotic Cell Model Labeled - 8 images - eukaryotic cell parts ... Prokaryotic Cell Model Labeled. Here are a number of highest rated Prokaryotic Cell Model Labeled pictures upon internet. We identified it from honorable source. Its submitted by handing out in the best field. We assume this kind of Prokaryotic Cell Model Labeled graphic could possibly be the most trending topic next we part it in google plus ...
Prokaryotic Cell: Definition, Functions, Diagram, Examples - Embibe Exams Prokaryotic cells are the unicellular cells that lack a well-defined nucleus, i.e. genetic material is not enclosed by a nuclear membrane. These cells are very minute in size \ (0.1\) to \ (5.0\, {\rm {\mu m}}\). Common prokaryotic cell is a bacterial cell. Our body has over \ (100\) trillion bacterial cells.
30. 9) To complete this Venn Diagram, label the following cell parts as ... 30. 9) To complete this Venn Diagram, label the following cell parts as A (Prokaryotic), B (common to both) or C (Eukaryotic) characteristics: A B C Prokaryotic Eukaryotic capsule flagella cell wall (incl. plants) cytoplasm cell membrane nucleus cell wall is B cytoplasm is B nucleus is C ajmoyar06 is waiting for your help.
Plant Cell- Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram Eukaryotic cell sediment in the 90s while prokaryotic cell sediment in the 70s. Ribosomes found in the mitochondria and chloroplasts are as small as the prokaryotic ribosomes. Naturally, ribosomes are made up of two subunits i. e small and large subunits, both classified according to their sedimentation rates by the S unit.
Eukaryotic Cells MCQ Quiz! - ProProfs Quiz Centrioles. 8. Prokaryotes are different from eukaryotic cells because they do not have membrane-bound nuclei. A. True. B. False. 9. Eukaryotic cells cannot produce energy.
Eukaryotic Cells: Definition, Diagram, and Examples - Research Tweet Microorganism are divided into Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes. Organism that do not possess nucleus and lack organelles are called prokaryotes. Eukaryotic cells are those who contains nucleus as well as the organelles. Example of prokaryotes are Archaea and Eubacteria. Eukaryotic organism examples are Algae, Fungi, Plants, Protists and Animals.















:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-prokaryotes-and-eukaryotes-129478-v41-5b69b4c546e0fb0025628d06.png)







Post a Comment for "40 prokaryotic cells label"