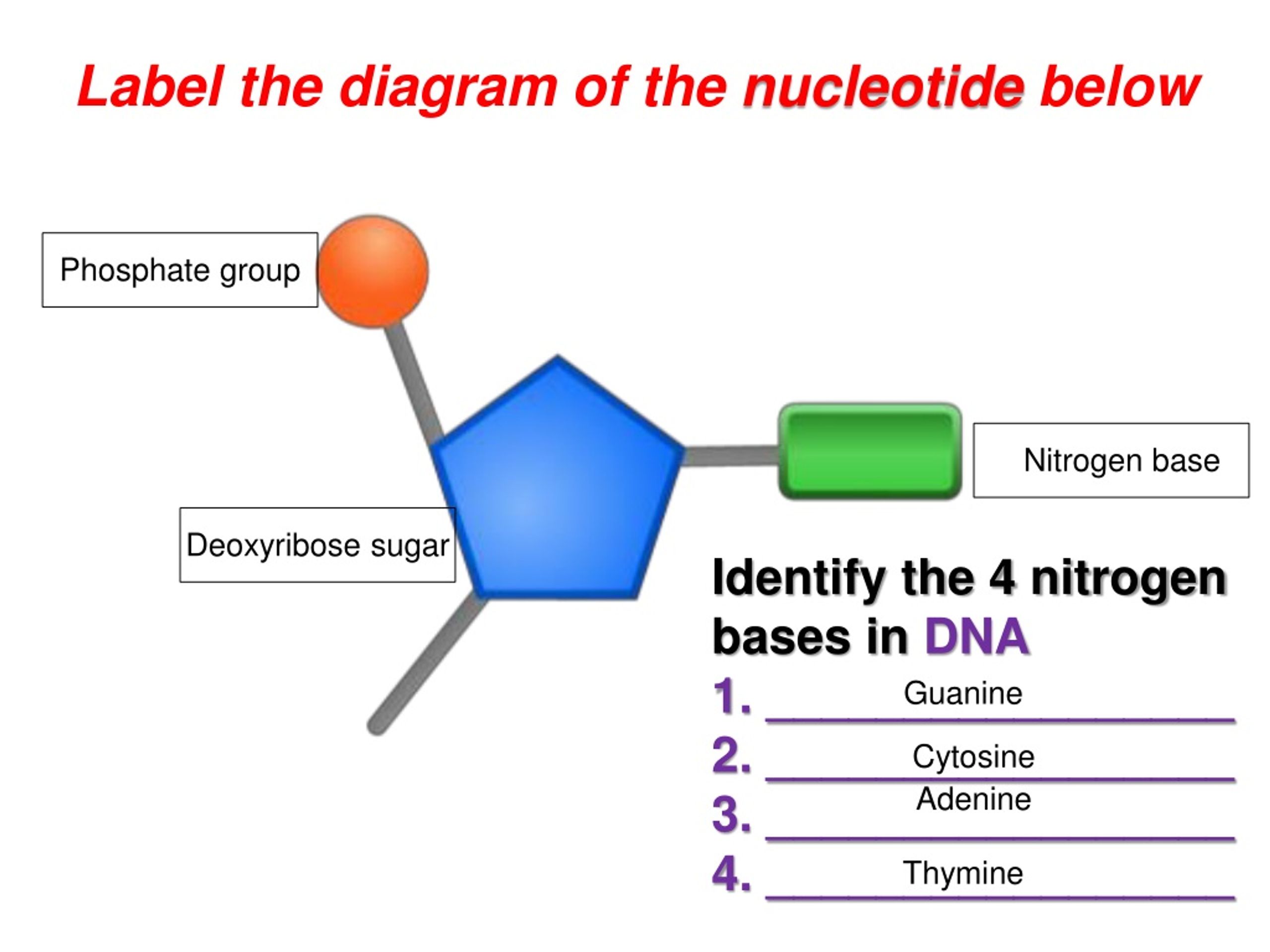
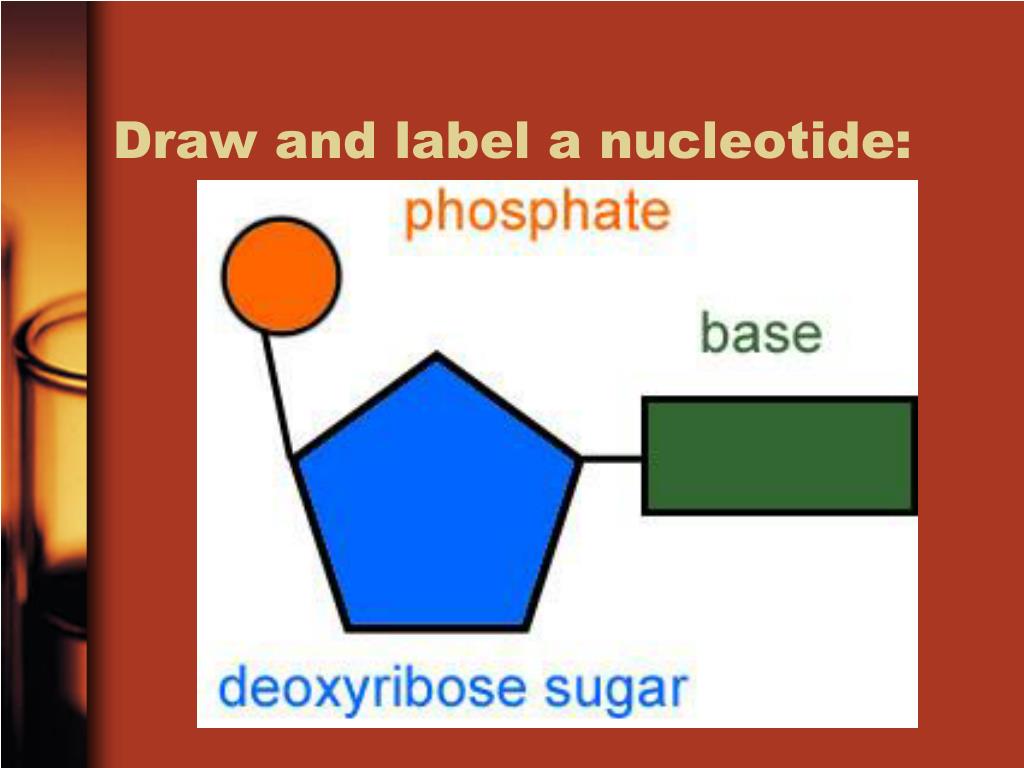
39 label of a nucleotide
Ivabradine: MedlinePlus Drug Information Ivabradine is in a class of medications called hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channel blockers. It works by slowing the heart rate so the heart can pump more blood through the body each time it beats. How should this medicine be used? Ivabradine comes as a tablet and as an oral solution (liquid) to take by mouth. It is usually taken with food twice a day. … The 5 Kinds of Nucleotides - ThoughtCo The five bases are adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, and uracil, which have the symbols A, G, C, T, and U, respectively. The name of the base is generally used as the name of the nucleotide, although this is technically incorrect. The bases combine with the sugar to make the nucleotides adenosine, guanosine, cytidine, thymidine, and uridine.
Solved Correctly label the parts of the two-nucleotide - Chegg Expert Answer. 100% (33 ratings) Transcribed image text: Correctly label the parts of the two-nucleotide nucleic acid depicted Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets Reset Help 5' position H2C OH in RNA Nitrogen base attached to 1' position 3' position Phosphodiester bond Deoxyribose 2 Phosphate Base.
Label of a nucleotide
What Is a Nucleotide? Definition, Structure, and Function The type of nucleotide is defined by its chemical base. There are five chemical bases: Adenine Cytosine Guanine Thymine Uracil The base and the amount of phosphate residue define how the compound is named. For example, an Adenine nucleotide with one phosphate group is called adenosine monophosphate. DNA Labeling - NEB Nucleic acids are readily labeled with tags that facilitate detection or purification. A variety of enzymatic or chemical methods are available to generate ... How do you draw a nucleotide and label its three basic parts? The above structure is a nucleotide. It consists of a: phosphate group; 5-carbon sugar, and; nitrogenous base. solution. expand. Was this answer helpful?
Label of a nucleotide. Nucleotide and Structural Label Identification in Single RNA Molecules ... Here we present a method for direct nucleotide identification and structural label mapping of single RNA molecules via Quantum Molecular Sequencing (QMSeq). The method combines non-perturbative quantum tunneling spectroscopy to probe the molecular orbitals of ribonucleotides, new experimental biophysical parameters that fingerprint these ... Home - Nucleotide - NCBI The Nucleotide database is a collection of sequences from several sources, including GenBank, RefSeq, TPA and PDB. Genome, gene and transcript sequence data provide the foundation for biomedical research and discovery. Nucleotides | Types, Examples, Functions & Classification Adenosine triphosphate (known as ATP) is the ideal example of a nucleotide. It contains three phosphate groups, a ribose sugar and adenine as base. It is known as the energy currency of the cell. It not only provides energy to various metabolic processes but also captures energy released in different reactions. DNA and RNA Probe Labeling | Radiolabeled Nucleotides Oligonucleotides can be labeled at either the 3' or the 5' end. Using polynucleotide kinase and ATP-gamma-32P, the 5' end is labeled. Using terminal transferase ...
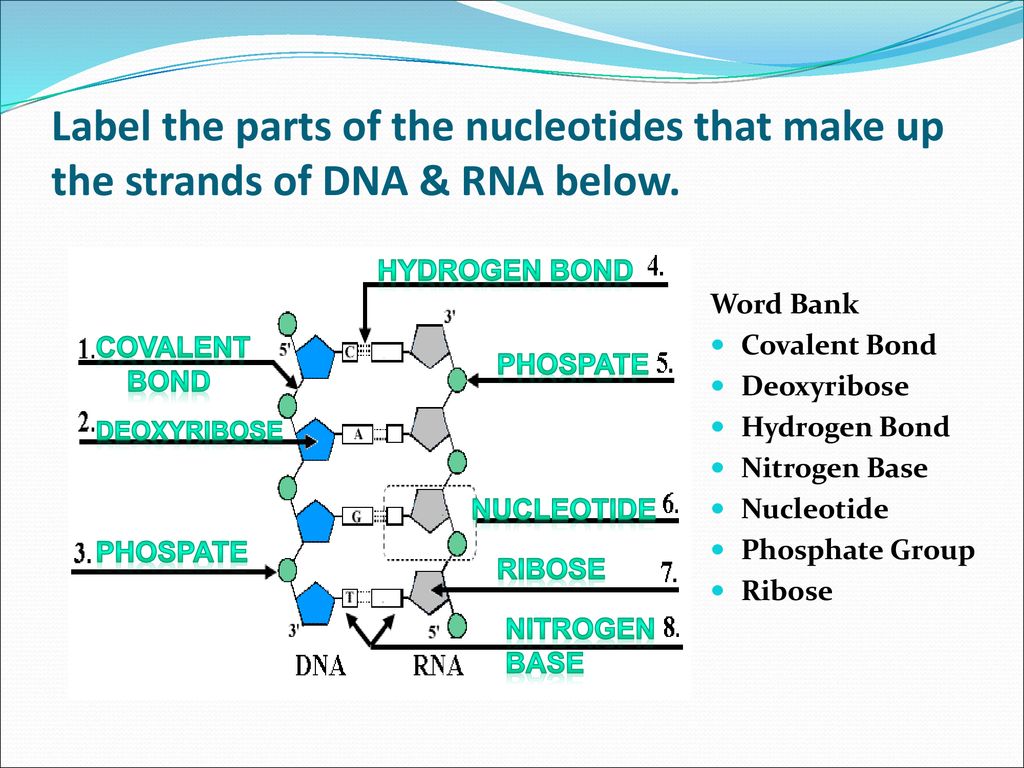
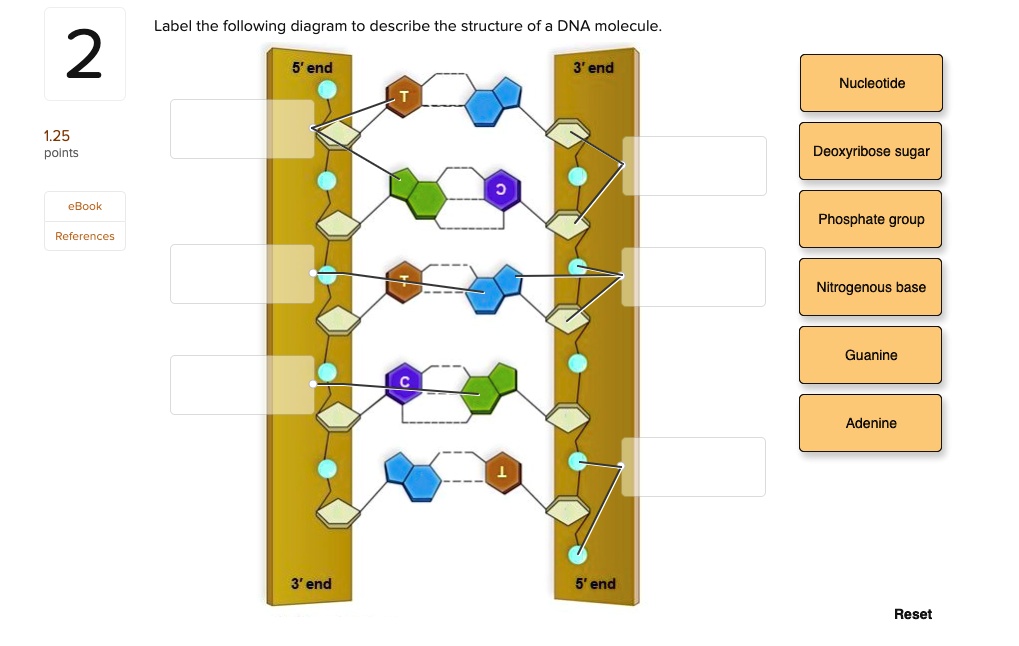
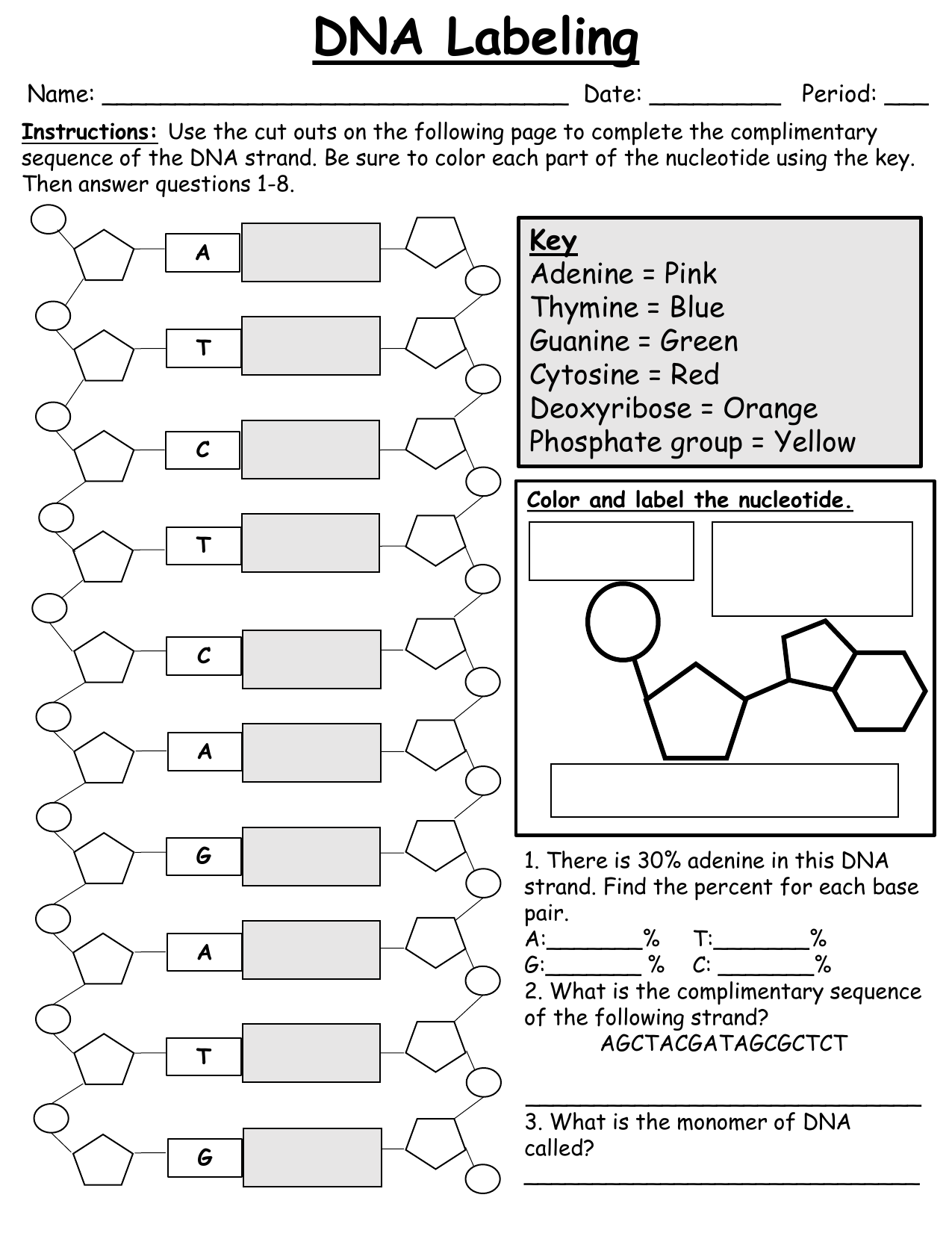
Nucleotides - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics 7.6.6 Nucleotides. Nucleotides are bio-chemicals found in mothers' milk consisting of one molecule of phosphoric acid, one molecule of sugar (ribose or dextrose) and one molecule of a purine or pyrimidine. In all, there are five nucleotides produced enzymatically. Nucleotides have been added to some infant formulations to simulate mothers ... Use the drop-down menus to label the parts of a nucleotide. A nucleotide is a molecule composed of a pentose sugar (ribose in RNA and deoxyribose in DNA), a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group. In DNA, there are four types of nucleotides that contain four different classes of nitrogen bases: Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Thymine. In RNA, Thymine bases are replaced by Uracil bases. Labeling Oligonucleotides and Nucleic Acids—Section 8.2 the labeled aha-dutp and aha-dctp nucleotides can be used to generate labeled nucleic acid hybridization probes for many molecular biology and molecular cytogenetics applications, including two-color microarray assays, northern and southern blots, colony and plaque hybridizations, dna sequencing, primer extension, dna and rna amplification and … draw a nucleotide and label the three parts - bestpriceheartbeads A nucleotide has three parts. In rna uracil is used in place of thymine. Draw and label a segment of dna showing its helix and complementary. If a specimen is made up of 30 adenine how much cytosine will it have. Once you have your 6 nucleotides pick up one of your A nucleotides yellow. List 3 differences between DNA and RNA 4.
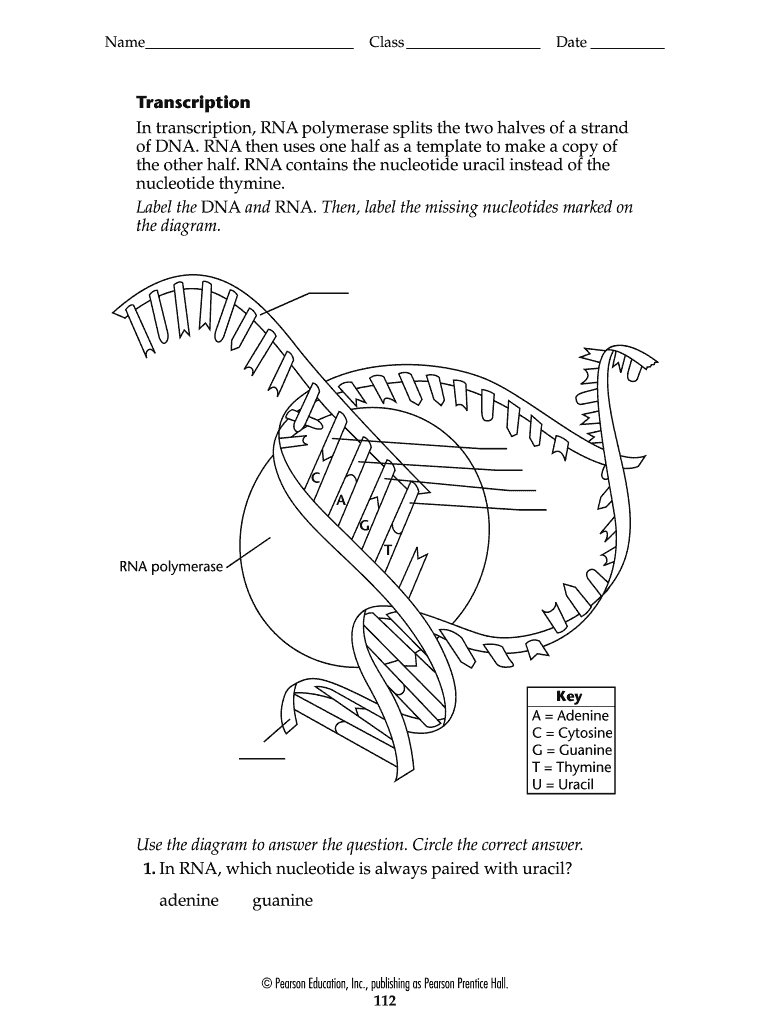
What are the Three Parts of a Nucleotide? | Albert.io Nucleotides are made up of 3 parts. The first is a distinct nitrogenous base, which is adenine, cytosine, guanine or thymine. In RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil. These nitrogenous bases are either purines or pyrimidines. Base pairs are formed when adenine forms a hydrogen bond with thymine, or cytosine forms a hydrogen bond with guanine. PAIN - LWW PAIN is issuing calls for papers relevant to the global COVID-19 pandemic. P AIN is seeking both basic and applied science papers addressing pain-related topics of importance to the pandemic. PAIN seeks submissions that fit the following types of articles: Clinical and Basic Science Research Reports, Clinical Notes, Epidemiology, Comprehensive Reviews, Narrative Reviews, … DNA and RNA Probe Labeling | Radiolabeled Nucleotides Our radionucleotides are labeled on either the alpha phosphate group, or the gamma phosphate group. This designation does not refer to the type of energy that is emitted. 32 P and 35 S are all beta-emitters (they give off beta energy in the form of beta particles). 3 Parts of a Nucleotide and How They Are Connected Here's the answer for both DNA and RNA . Nucleotides in DNA and RNA Both deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are made up of nucleotides which consist of three parts: Nitrogenous Base Purines and pyrimidines are the two categories of nitrogenous bases. Adenine and guanine are purines. Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines.
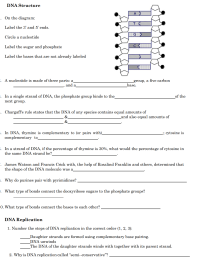
Solved 1. Draw a DNA nucleotide & an RNA nucleotide. | Chegg.com 1. Draw a DNA nucleotide & an RNA nucleotide. Label each of the 3 major parts. 3. What is the point of DNA replication? _____ 4.
Genetic Linkage - University of Utah To see how linkage works, let's look at some specific genes. Two of the genes (1 and 2) are relatively far apart (top illustration). Each gene comes in two different versions, or alleles: A and B.
Label-free genotyping of single-nucleotide polymorphisms for DNA and ... By using the specific primer extension reaction, a new assay for genotyping of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) has been demonstrated. The assay relies on the conformational and colorimetric change of water-soluble polythiophene derivative, poly[3-(3'-N,N,N-triethylamino-1'-propyloxy)-4-methyl-2,5-thiophene hydrochloride] (PMNT), upon forming interpolyelectrolyte complex with extended ...
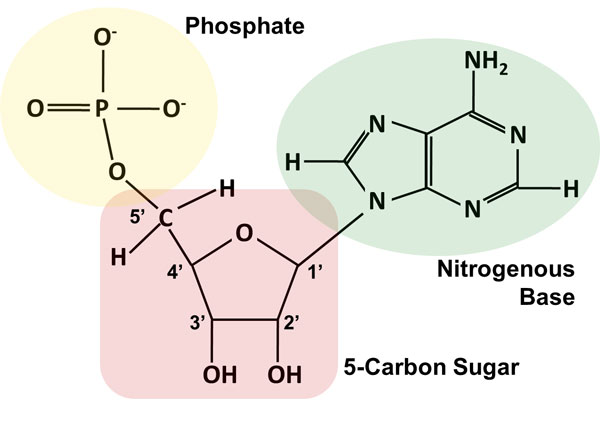
Nucleotide - Wikipedia A nucleotide is composed of three distinctive chemical sub-units: a five-carbon sugar molecule, a nucleobase—the two of which together are called a nucleoside—and one phosphate group.With all three joined, a nucleotide is also termed a "nucleoside monophosphate", "nucleoside diphosphate" or "nucleoside triphosphate", depending on how many phosphates make up the phosphate group.
Building Blocks of Nucleic Acids | Structures & Functions Phoebus Levene (American Biochemist - Image: Wikimedia) DNA and RNA are both made up of small building blocks called nucleotides.These units are covalently linked: between the phosphate group of the fifth carbon of one nucleotide to the pentose sugar. attached to the third carbon of the second nucleotide.. Series of these covalent linkages among nucleotide units form the polymer nucleic acids.
Nucleotide and structural label identification in single ... - NCBI by GR Abel Jr · 2019 · Cited by 5 — Here we present a method for direct nucleotide identification and structural label mapping of single RNA molecules via Quantum Molecular Sequencing (QMSeq).
Nucleotide: Structure, Examples and Function - BYJUS A nucleotide is an organic molecule with a basic composition of a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar and phosphate. DNA and RNA are polynucleotides, which contain a chain of nucleotides monomers with different nitrogenous bases. Nucleotides are essential for carrying out metabolic and physiological activities.
Nucleotide - Definition, Structure (3 Parts), Examples & Function A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of DNA and RNA. They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. A nucleotide is made up of three parts: a phosphate group, a 5-carbon sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine.
How do you draw a nucleotide and label its three basic parts? Explanation: The above structure is a nucleotide. It consists of a: phosphate group. 5-carbon sugar, and. nitrogenous base.
Nucleotide Structure: DNA Diagram | Science Trends Nucleotides are made out of elements like nitrogen and carbon with a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar component, and a group of phosphates. However, there are some important differences between RNA nucleotides and DNA nucleotides. The nitrogenous bases come in one of two different forms - they are either a pyrimidine or a purine.
What is Nucleotide? Definition, Properties, Components ... - Biology Reader A nucleotide is a compound, which can form a polynucleotide chain by the union of nitrogenous bases and sugar-phosphate group. Monomers of nucleotide units are connected via a covalent phosphodiester bond. Nitrogenous bases, i.e. purines and pyrimidine, are attached via weak hydrogen bonds. The bases link with a deoxyribose pentose sugar via an ...
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION VALTREX monophosphate, a nucleotide analogue. The monophosphate is further converted into diphosphate by cellular guanylate kinase and into triphosphate by a number of cellular enzymes. In vitro, acyclovir triphosphate stops replication of herpes viral DNA. This is accomplished in 3 ways: 1) competitive inhibition of viral DNA polymerase, 2) incorporation and termination of the …
Methods for Labeling Nucleic Acids | Thermo Fisher Scientific Common labels used to generate nucleic acid probes include radioactive phosphates, biotin, fluorophores and enzymes.
Nucleotide - Genome.gov A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (RNA and DNA). A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T).
Metformin - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf 02/05/2022 · Metformin, FDA-approved in 1994, is an antidiabetic agent used in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metformin comes in both immediate-release and extended-release and is used in several combination products with other antidiabetic agents. Metformin also has several non-FDA-approved indications, including gestational diabetes, management of antipsychotic-induced …
What are the three parts of a nucleotide? Flashcards | Quizlet Nucleotide. basic unit. surgery in DNA. deoxylibonuelic. hydrogen bonds. hold DNA together. covalent bond is. sharing of electrons. ionic is the attraction between. 2 ions. 4 nitrogen bases. cytosine, thymine, adenine, guanine. DNA is a. polymer. A polymer is a _____ that is made of _____
FoundationOne Liquid CDx Technical Information single nucleotide variants (SNVs) <0.21% VAF and in patients with . MET . indels <0.16% VAF tested with FoundationOne Liquid CDx. Page . 4 . of . 53 . RAL-0035-03 • The precision of FoundationOne Liquid CDx was only confirmed for select variants at the limit of detection. • The FoundationOne Liquid CDx assay does not detect heterozygous deletions. • The …
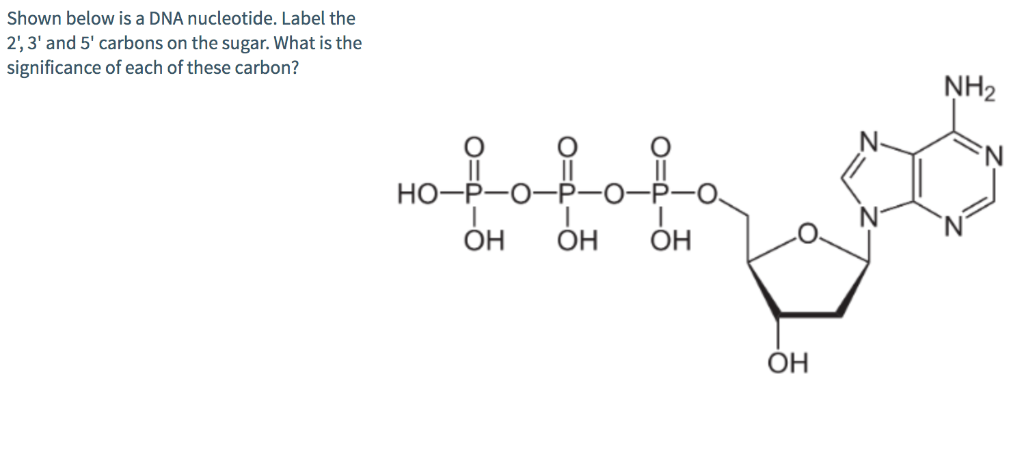
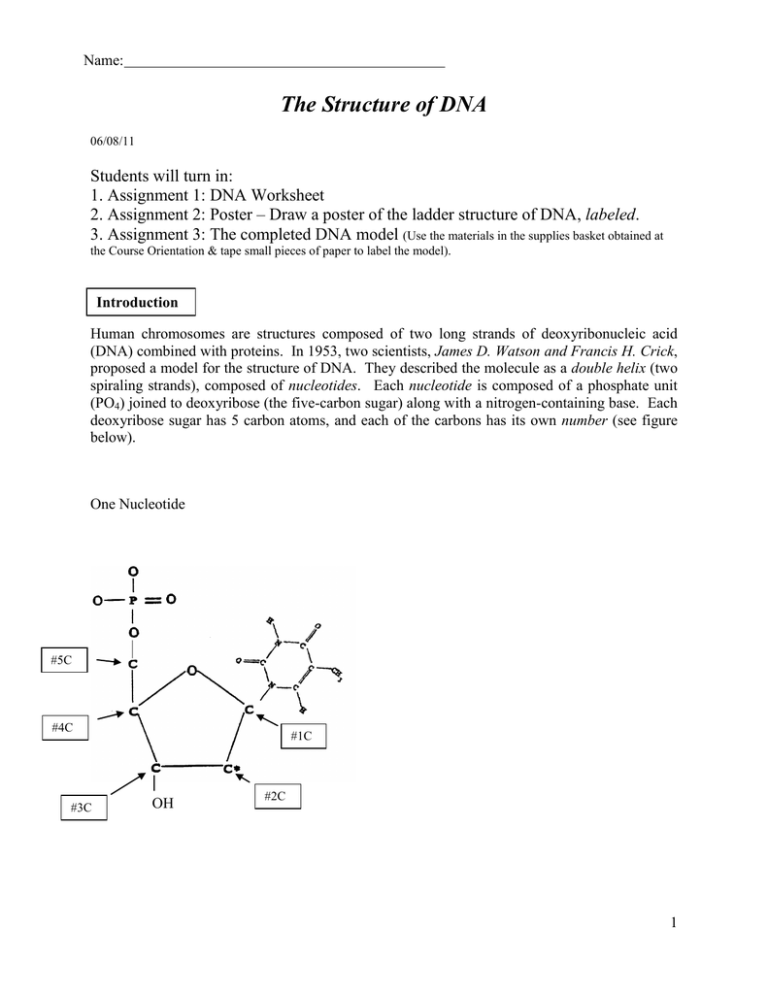
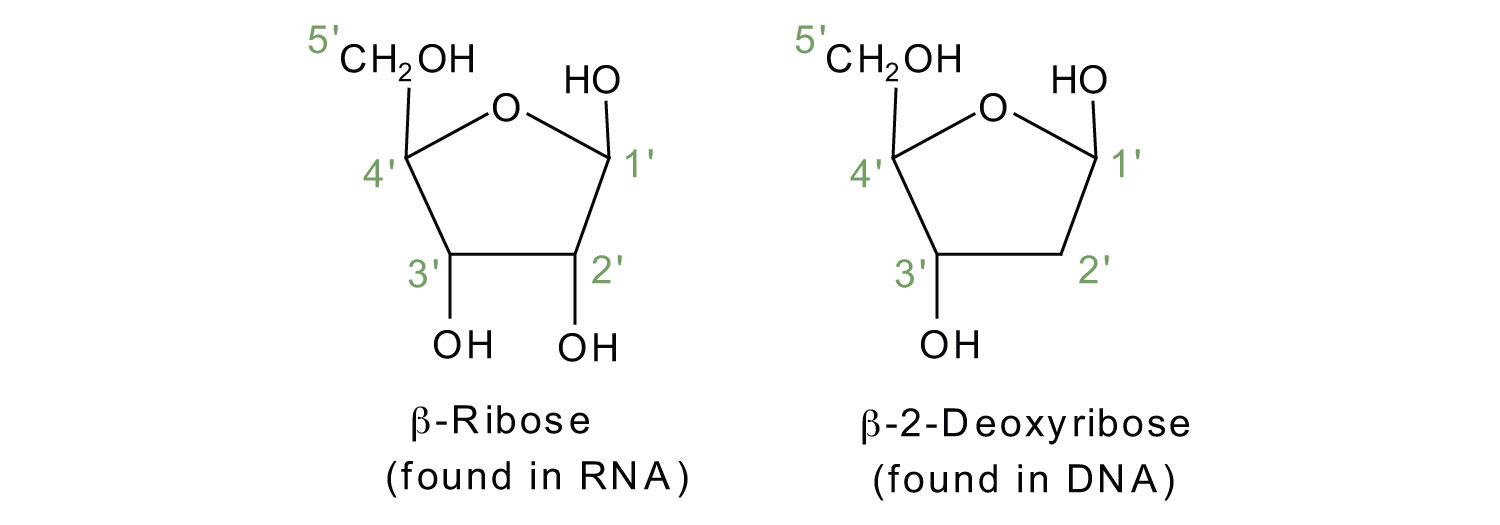
Nucleotides in DNA | Science Primer DNA is a nucleotide polymer, or polynucleotide. Each nucleotide contains three components: A five carbon sugar A phosphate molecule A nitrogen-containing base. The sugar carbon atoms are numbered 1 to 5. The nitrogenous base attaches to base 1, and the phosphate group attaches to base 5. DNA polymers are strings of nucleotides.
DNA Molecule Label Diagram | Quizlet the nucleotide that hydrogen bonds with the nucleotide thymine in DNA or with uracil in RNA Guamine found in DNA and RNA; always bonds with a Cytosine Nucleotide in a nucleic-acid chain, a sub-unit that consists of a sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base Cytosine The base that pairs with Guanine with DNA Base Pair
Tools of EzBioCloud Orthologous Average Nucleotide Identity Tool (OAT) is a standalone software used to perform OrthoANI algorithm and BLAST calculations to measure the overall similarity between two genomes sequences. Visit the tool's main page here . ContEst16S. ContEst16S is a web service that enables the detection of potential contaminants in your bacterial or archaeal draft genome …
BankIt Submission Help: Feature Table File The first line of the feature table contains the following basic information >Feature Sequence_ID The sequence identifier (Sequence_ID) must match the label used to identify each table's corresponding sequence in the nucleotide FASTA file. Subsequent lines of the table list the features. Prepare the feature table file in a text editor and save it as plain ascii text (not .rtf or …
How (and Why) to Label Nucleic Acids - Bitesize Bio Mar 27, 2019 — The most common labels are fluorescent 'tags' that are synthesized and incorporated into oligonucleotides, but you can also attach a variety of ...
The Structure of DNA Each nucleotide is itself make of three subunits: A five carbon sugar called deoxyribose (Labeled S) A phosphate group (a phosphorous atom surrounded by four oxygen atoms.) (Labeled P) And one of four nitrogen-containing molecules called nucleotides . (Labeled A, T, C, or G)
n the diagram to the right, identify the three components of a ... * A nucleotide variable depending on the type of nucleotide (purine or pyrimidine) attached to the carbon 1' of the pentose; * pentose: a sugar with five carbon atoms ; * a phosphate group (or phosphoric acid), identical for the nucleotides of DNA and RNA, attached to the 5 'carbon atom of the pentose, and to the 3' carbon atom of the ...
How do you draw a nucleotide and label its three basic parts? The above structure is a nucleotide. It consists of a: phosphate group; 5-carbon sugar, and; nitrogenous base. solution. expand. Was this answer helpful?
DNA Labeling - NEB Nucleic acids are readily labeled with tags that facilitate detection or purification. A variety of enzymatic or chemical methods are available to generate ...
What Is a Nucleotide? Definition, Structure, and Function The type of nucleotide is defined by its chemical base. There are five chemical bases: Adenine Cytosine Guanine Thymine Uracil The base and the amount of phosphate residue define how the compound is named. For example, an Adenine nucleotide with one phosphate group is called adenosine monophosphate.





















Post a Comment for "39 label of a nucleotide"